- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-29 Origin: Site









An oil-bath air filter helps you protect your engine from dust and dirt. You pull air through the oil bath air filter, where the air passes over oil and traps heavy particles. The oil bath air cleaners use a special filtration process. Fine particles stick to the filter mesh, which the oil coats. You get cleaner air for your engine. Oil bath air cleaners and oil-bath air filters work well in harsh environments. If you want to know how they work, you need to understand this filter’s role in engine care.
Using the right filter keeps your engine running longer and stronger.
Oil-bath air filters trap dust and dirt using oil and mesh, protecting engines in dusty and harsh environments.
These filters last longer and save money because you can clean and reuse them instead of replacing them often.
Regular maintenance, including cleaning and changing the oil, keeps the filter working well and extends engine life.
Oil-bath air filters work best in heavy-duty machines like tractors, construction equipment, and diesel generators.
Using the right oil and avoiding overfilling prevents problems like engine smoke and keeps your filter efficient.
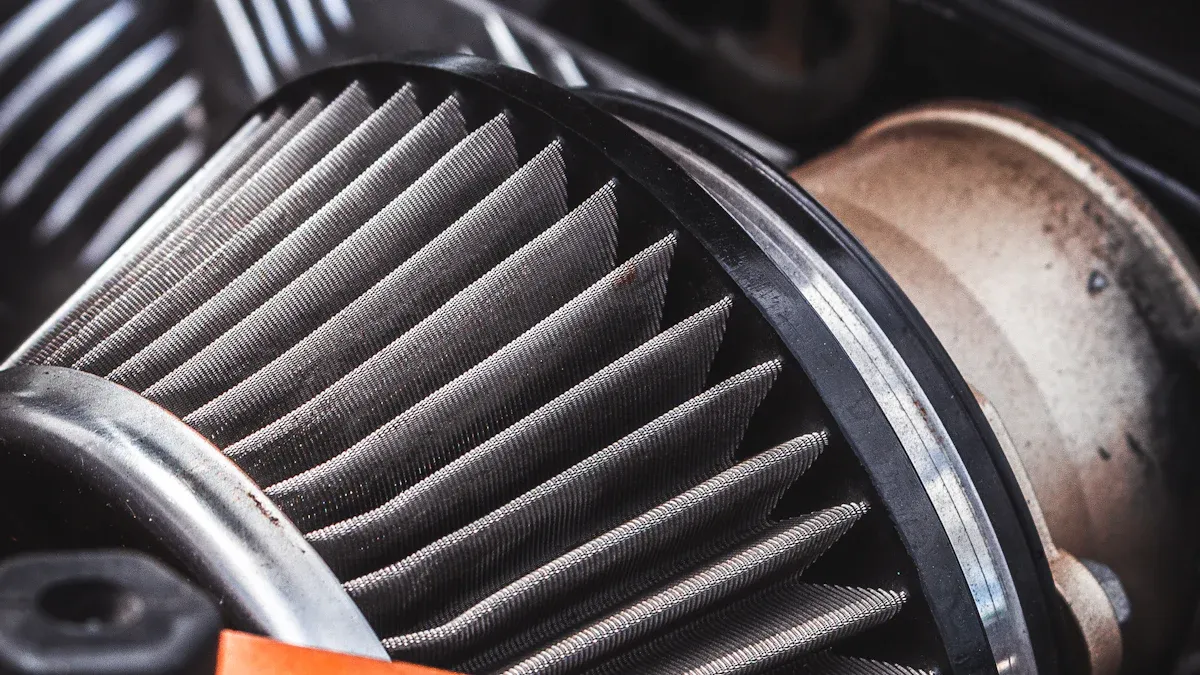

You start the process when air enters the oil-bath air filter from the top of the filter case. The design slows the airflow and reverses its direction above the oil surface. This change causes larger and heavier dirt particles to drop into the oil. The working principle of the oil bath air filter relies on this initial step to absorb dust and impurities before the air moves further. Oil bath air cleaners use this two-stage filtration process to remove particles greater than 10 micrometers by inertial impaction and adhesion in the oil sump.
Tip: The air intake design helps your filter handle high dust loads without clogging quickly.
As air flows over the oil bath, the oil traps dirt and dust by adhesion and viscous impingement. The oil’s viscosity causes particles to stick and stay in the reservoir. You benefit from this process because the oil bath air filter can hold a large amount of dirt, making it ideal for harsh and dusty environments. The oil bath air cleaners rely on the oil’s ability to capture contaminants before the air reaches the filter element. Thinner oils work best in larger, externally mounted filters, such as those found in heavy trucks, because they reduce the risk of oil entering the engine and improve filtration performance.
After passing through the oil bath, the air moves upward toward the filter element. Most oil-bath air filters use steel wool, oiled gauze made from cotton or synthetic fibers, or oiled foam. These materials allow high airflow while the oil coating captures finer particles. The filter element is always wet with oil, which increases its ability to absorb dust and impurities. Oil bath air cleaners use this mesh or gauze to trap the smallest and lightest particles before the air enters the engine. You need to clean and re-oil the filter element regularly to maintain filtration efficiency.
Common filter element materials:
Steel wire mesh
Oiled cotton gauze
Synthetic fibers
Oiled foam
The final step in the oil bath air filter operation delivers clean air to your engine. The filter removes most dirt and dust, but some fine particles may still pass through. In controlled tests, oil-bath air filters achieve filtration efficiency between 95.4% and 98.6%. Paper filters reach higher efficiency, but oil bath air cleaners excel in dirt holding capacity and durability in harsh environments. You get reliable engine protection, especially when you drive in dusty or abrasive conditions.
Filter Type | Filtration Efficiency (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Oil-bath air filter | 95.4 - 98.6 | High dirt holding capacity, durable in harsh environments |
Paper filter | 99.95+ | Highest efficiency, clogs faster in dirty conditions |
Oiled foam/gauze | 95 - 99 | Comparable to oil-bath, less dirt holding capacity |
Note: Oil bath air filters may allow some dirt to enter engine oil, but they protect engines better in extremely dusty environments by not clogging as quickly as paper filters.
You now understand how they work and why oil bath air filters remain valuable for engine protection in tough conditions.
You find diesel engine oil bath air filters in many types of machinery that work in tough environments. These filters protect engines from dust and dirt, especially where dry paper filters would clog quickly. You see oil bath air cleaners on construction equipment, farm machines, and industrial generators. They also appear on diesel water pumps and welding generators. Many single-cylinder, four-stroke, air-cooled diesel engines use this type of filter. Tractor oil bath air filters are common on older agricultural equipment because they handle heavy dust loads.
Here is a table showing where you often find these filters:
Diesel Engine and Machinery Types | Description |
|---|---|
Air-cooled Diesel Generator Series | Includes open frame, silent type, two-cylinder models |
Diesel Water Pump Series | Used in diesel-driven water pumps |
Industrial Generator Series | Various industrial generators |
Air-cooled Diesel Welding Generator Series | Generators used for welding applications |
Construction Machinery Series | Plate compactors, concrete vibrators, power trowels, power saws, rammers, high pressure washers |
Farm Machinery | Various agricultural machines |
Engine Type | Single-cylinder, four-stroke, air-cooled diesel engines |
You often see oil bath air cleaners in places with high dust levels. Construction sites, agricultural fields, and old diesel engine applications rely on these filters. The oil bath traps dust and debris, keeping engines safe and running smoothly. You benefit from their stable filtering effect and long service life. These filters work well in heavy machinery that faces harsh conditions every day.
Tip: If you operate equipment in dusty fields or on construction sites, you should choose a diesel engine oil bath air filter for better protection and longer engine life.
You get several advantages when you use oil bath air cleaners in diesel engines. These filters perform better than paper and foam filters in extremely dusty or ash-filled environments. For example, during the Mt Saint Helens eruption, paper filters clogged immediately, but oil bath air cleaners kept engines running. You can clean and service these filters at home by refreshing the oil. Paper filters clog quickly and cannot be cleaned effectively. Oil bath air cleaners trap debris efficiently and last longer in heavy dust conditions, such as on diesel tractors and trucks in agricultural fields.
Here are the main advantages:
You clean and reuse the filter, saving money over time.
Oil bath air cleaners are more durable in harsh, dusty environments.
You maintain the filter by topping up or changing the oil, which extends its service life.
These filters reduce engine wear and lower emissions by trapping dust and particulate matter before it enters the engine.
You get reliable performance in heavy-duty applications, even when maintenance is frequent.
Oil bath air filters require regular cleaning and oil changes, especially if you use your equipment heavily. You need to remove the filter, wash it, dry it, and reapply the correct oil. This process takes time and effort, but it keeps your filter working efficiently. Paper filters are easier to replace and need no cleaning, which makes them practical for fleets and modern machinery. Foam filters require similar maintenance to oil bath air cleaners, but they are less common in diesel engine applications.
When you compare costs, oil bath air cleaners have a higher upfront price. However, you save money over the life of your engine because you reuse the filter instead of buying new ones. Dry filters cost less at first but need replacement every 12,000 to 15,000 miles. If you maintain your diesel engine oil bath air filter, it can last for hundreds of thousands of miles. You spend less on replacements and keep your engine protected.
Oil bath air cleaners also help reduce engine emissions. The oil traps dust and particles, keeping them out of the combustion chamber. You get cleaner air for your engine, which improves performance and lowers emissions. This benefit is important for diesel-powered equipment that operates in tough conditions.
Note: If you want a filter that lasts, saves money, and protects your engine in dusty environments, you should consider using a diesel engine oil bath air filter.
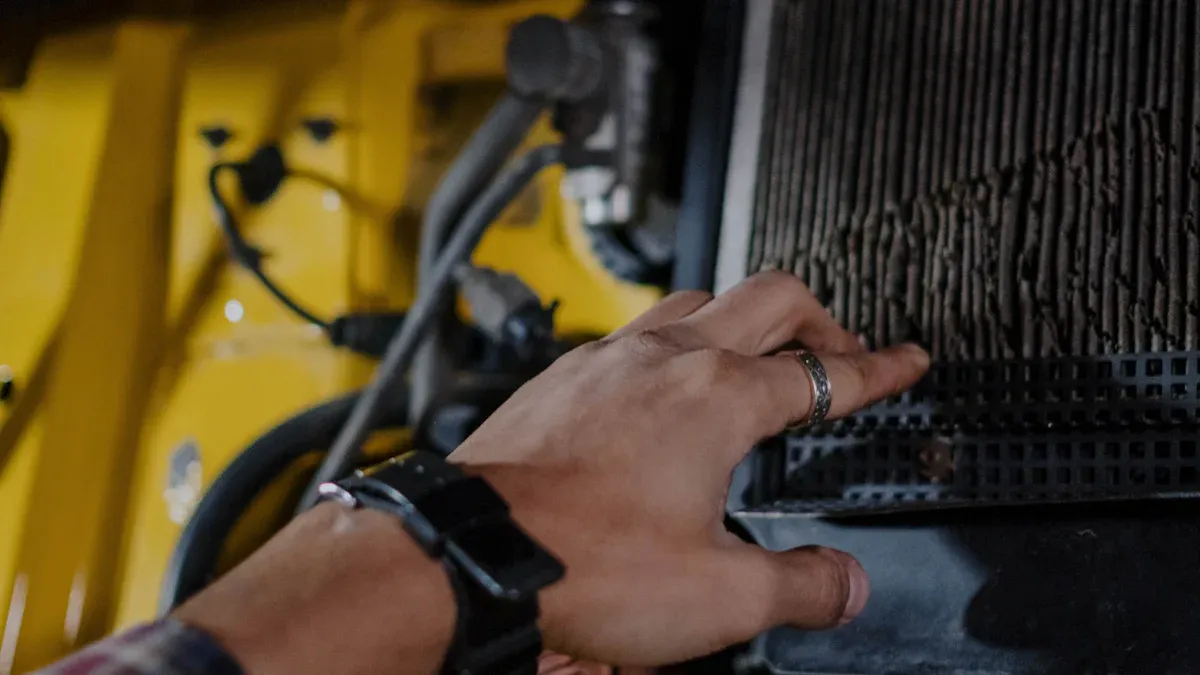
Choosing the right oil for your oil-bath air filter helps you keep your engine safe. Most engine manufacturers recommend using the same type and weight of oil in the filter as you use in your engine. You should match the oil weight to the temperature where you operate your equipment. Many users prefer new engine oil, including synthetic multi-weight oils like 15W-40, because these oils work well in modern engines and filters. Hydraulic oil can serve as an alternative, but you should avoid gear oil, especially in cold weather. You do not need a special brand; just make sure the oil fits your engine’s needs and the climate. Change the oil in your filter at least once a year or more often if you use your equipment in dusty conditions.
Tip: Always check your owner’s manual for the recommended oil type and change intervals for your oil-bath air filter.
Regular cleaning keeps your filter working at its best. You should let your engine sit for at least ten minutes before starting maintenance so the oil settles. Remove the filter basin and element carefully to avoid damaging the gasket. Pour out the dirty oil and sludge, then clean the basin thoroughly. Soak the filter element in diesel oil and let it drip dry. Clean the casing if it looks dirty. Inspect all gaskets and replace any that look worn or damaged. Refill the basin with the same oil you use in your engine, making sure not to exceed the marked level. Reassemble the filter and tighten all clamps and bolts. In heavy-duty or off-road use, clean your filter every 3,000 to 5,000 miles. Always inspect the filter at every oil change. If the filter media looks dark or matted, clean it right away.
Step | Maintenance Action |
|---|---|
1 | Stop engine, let oil settle |
2 | Remove basin and element |
3 | Drain dirty oil and sludge |
4 | Clean basin and element |
5 | Inspect and replace gaskets |
6 | Refill with correct oil |
7 | Reassemble and tighten |
You may face several problems with oil-bath air filters. If the oil level is too high, oil can get sucked into the engine, causing blue smoke and fouled spark plugs. Oil should never touch the wire mesh inside the filter. Bulky filter designs can retain heat, which may lead to vapor lock or fuel boiling. Over-oiling can cause oil aerosol to coat sensors, leading to poor fuel economy or rough idle. Maintenance requirements for oil bath air filter systems can be demanding, especially in dusty environments. Improper cleaning, using harsh chemicals, or not drying parts well can damage the filter. Always check for damaged mesh, cracked bowls, or worn gaskets. If you notice reduced airflow or contamination, inspect and clean the filter immediately. Dispose of used oil and cleaning materials responsibly.
Note: Regular inspection and careful cleaning help you avoid most common issues and keep your filter working efficiently.
Oil-bath air filters give you reliable engine protection in dusty conditions. You benefit from improved airflow, reusable design, and strong filtration when you maintain your filter regularly.
Oil-bath air filters trap dirt with tacky oil and mesh, supporting engine power and longevity.
You save money over time by cleaning and reusing your filter.
These filters remain essential for off-road, heavy-duty, and vintage vehicles.
Tip: Clean your oil-bath air filter often to keep your engine running smoothly and extend its life.
You use an Oil-bath Air Filter to trap dust and dirt before they reach your engine. The oil and filter mesh work together to keep harmful particles out, which helps your engine last longer.
You should check and clean your Oil-bath Air Filter every 3,000 to 5,000 miles. If you work in very dusty areas, clean it more often. Always follow your equipment’s manual for best results.
You should use the same oil type and weight as your engine oil. Most manufacturers recommend this for the best protection. Avoid gear oil or old, dirty oil. Always check your manual for the correct oil.
If you add too much oil, the Oil-bath Air Filter can let oil get sucked into the engine. This may cause blue smoke or fouled spark plugs. Always fill to the marked level only.
Oil-bath Air Filters work better in dusty or harsh environments. You can clean and reuse them, which saves money. Paper filters trap finer particles but clog faster and need replacement more often.